Beyond 90%: The Complex Role of Dopamine Regulation in Mental Health and Daily Life
A recent social media post by user BONESAW 🕊️ ignited discussion by stating, > "It's difficult to admit 90% of your problems can be traced back to poor dopamine regulation." This bold claim, while likely an oversimplification, highlights a growing public awareness of dopamine's profound influence on human behavior and mental well-being, a concept extensively explored in neuroscience. While the "90%" figure lacks scientific substantiation, research confirms dopamine dysregulation is a complex factor in a wide array of psychological and neurological conditions.
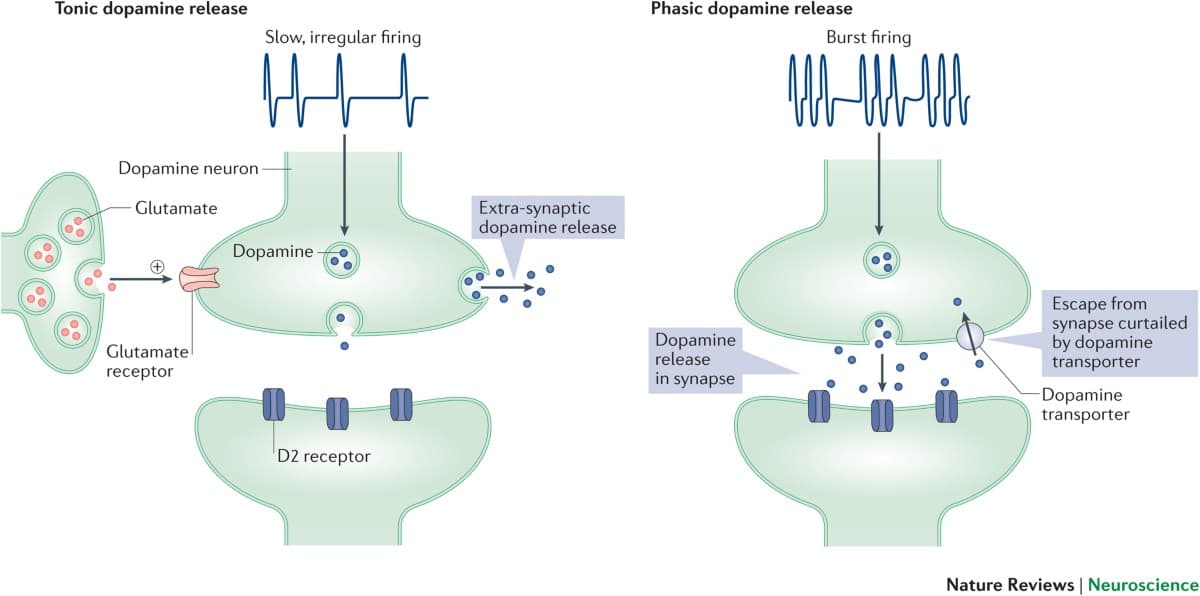
Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter, plays a pivotal role in the brain's reward system, motivation, pleasure, and motor control. It influences our ability to focus, learn, experience enjoyment, and respond to incentives. Disruptions in its intricate regulatory pathways can manifest in diverse ways, impacting daily functioning and contributing to various health challenges.
In Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), for instance, dopamine system downregulation is frequently linked to anhedonia, the inability to experience pleasure, a core symptom of depression. Studies indicate that effective antidepressant treatments, including novel approaches like ketamine, often modulate dopamine activity to alleviate these symptoms, highlighting its critical role in mood regulation.
Similarly, dopamine dysregulation is implicated in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and addiction. While ADHD is not simply a "dopamine deficiency," research points to complex alterations in dopamine signaling that affect attention and impulse control. In addiction, dopamine is central to reward, craving, and the heightened attention paid to drug-related cues, driving compulsive behaviors and the persistence of substance use disorders.
The assertion that 90% of problems stem from dopamine dysregulation oversimplifies a highly complex neurobiological system. Dopamine interacts intricately with other neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, and its effects can vary depending on brain region and specific receptor types. Genetic predispositions, environmental factors, and developmental experiences also profoundly shape dopamine system function.
Emerging research further connects dopamine to broader psychological aspects, such as attachment and creativity. Studies suggest that early adverse experiences, like childhood parental loss, can epigenetically influence dopamine pathways, affecting motivation and openness to new experiences. Continued scientific inquiry aims to unravel these intricate connections, paving the way for more targeted and effective interventions for a multitude of conditions where dopamine plays a significant, albeit complex, role.