Healthcare AI Market Projected to Reach $187 Billion by 2030, Co-founder Declares "FSD for Healthcare is Inevitable"
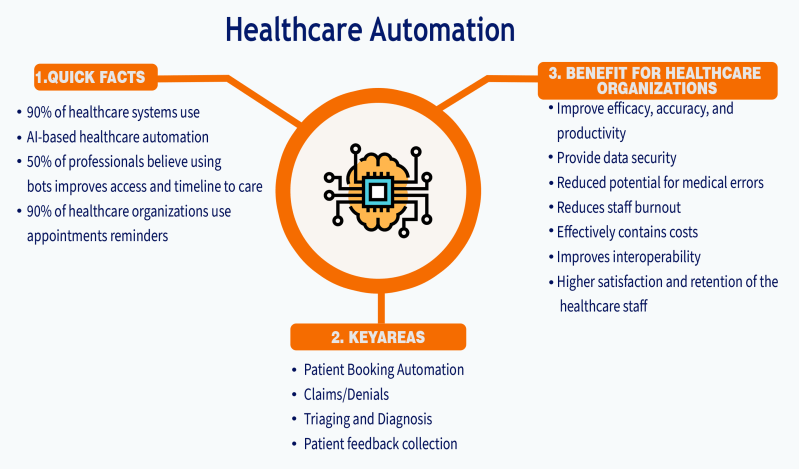
Arthur MacWaters, co-founder of AI-native psychiatry network Legion Health, recently asserted on social media that "FSD for healthcare is INEVITABLE," signaling a future where Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation achieve a level of pervasive, autonomous functionality akin to "Full Self-Driving" technology in vehicles. This bold statement underscores a rapidly accelerating trend, with the global AI in healthcare market projected to grow from approximately $19.27 billion in 2023 to nearly $188 billion by 2030.
The "inevitability" stems from AI's transformative impact across diagnostics, operations, and patient care. AI algorithms are already enhancing diagnostic precision in medical imaging, often matching or exceeding human experts in identifying conditions like breast cancer and diabetic retinopathy. Furthermore, predictive analytics powered by AI can forecast health risks, enabling earlier interventions and personalized treatment plans, moving healthcare towards a preventive model.
In administrative functions, AI-driven automation is significantly reducing burdens on healthcare staff. This includes streamlining tasks such as appointment scheduling, medical coding, billing, and clinical documentation, with generative AI tools automating note-taking during patient consultations. These efficiencies are crucial in addressing workforce shortages and allowing professionals to dedicate more time to direct patient interaction.
However, the widespread adoption of AI in healthcare is not without its challenges. Concerns surrounding data privacy and security, algorithmic bias, and the substantial costs of implementation remain prominent. Regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines, such as those proposed by the World Health Organization, are critical to ensuring responsible and equitable integration of these powerful technologies into the healthcare ecosystem.
As AI continues to mature, its role is expanding into areas like drug discovery, personalized medicine, and remote patient monitoring through wearables. The convergence of AI with other technologies is fostering "omni-medicine," a blend of in-person and virtual care, promising greater accessibility and efficiency. This ongoing evolution suggests that AI will indeed become an indispensable, "inevitable" component of future healthcare delivery.