Cloudflare Shifts Web Scraping Dynamics, Blocks AI Crawlers by Default Across 20% of Internet Traffic
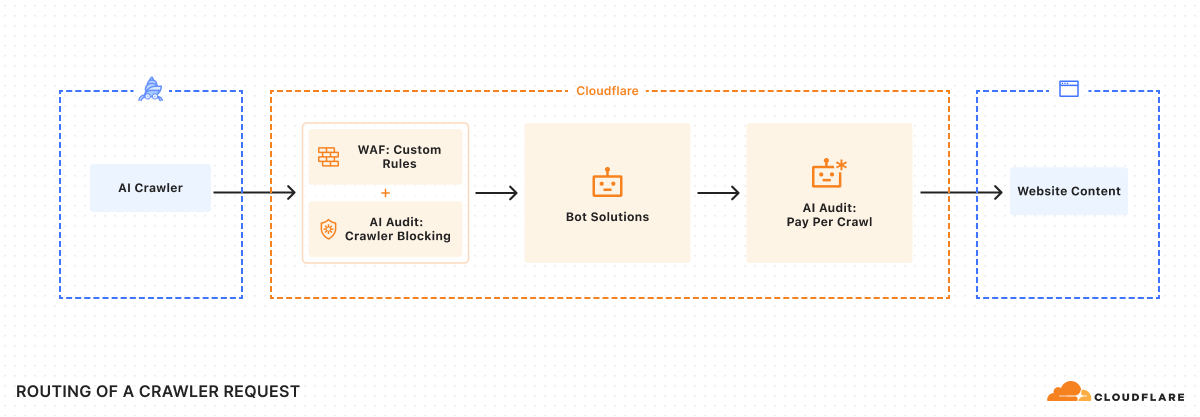
San Francisco, CA – Internet infrastructure giant Cloudflare, which processes approximately 20% of global web traffic, has implemented a new default policy to block artificial intelligence (AI) crawlers from accessing content without explicit permission or compensation. This significant move, effective July 1, 2025, fundamentally redefines the relationship between content creators and AI companies, particularly those relying on extensive web scraping for model training and data acquisition.
The shift addresses long-standing concerns from publishers and content creators regarding the uncompensated use of their data. Jon Stokes, a prominent commentator, underscored this perspective in a recent tweet, stating, > "Every one of these AI company browsers is about one thing & one only: web scraping. Cloudflare has shut down their ability to get tokens off the open web. Hence these browsers." This highlights the perceived primary purpose of AI-driven browsers.
Cloudflare's new approach mandates that new domains signing up for its services will have AI crawlers blocked by default, requiring website owners to actively grant permission. This reverses the previous "opt-out" model. Additionally, the company has introduced a "Pay Per Crawl" model, allowing publishers to set prices for AI companies to access their content, creating a potential new revenue stream for original content.
The initiative has garnered strong support from major media organizations including Condé Nast, The Associated Press, and TIME, who view it as a crucial step toward ensuring fair compensation and protecting intellectual property in the AI era. Matthew Prince, Cloudflare CEO, emphasized that the goal is to empower creators and safeguard the future of a vibrant internet.
However, not all AI companies are aligned with the new framework. OpenAI, for instance, has expressed reservations, suggesting that Cloudflare is inserting an unnecessary intermediary into the system. Cloudflare asserts its advanced bot management capabilities can effectively identify and block AI crawlers, even those attempting to spoof legitimate user agents, ensuring the new policies are robustly enforced. This development is expected to significantly impact how AI models acquire and utilize training data from the open web.