Hyperscalers Grapple with Energy Demands as China Faces AI Development Hurdles
A recent tweet by Aakash Gupta highlights critical discussions within the technology sector, pointing to challenges in China's artificial intelligence (AI) development, the energy choices of hyperscale data centers, and the complexities of measuring Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) impact. The tweet, which includes a link to further information, suggests a "masterclass" on these interconnected topics.
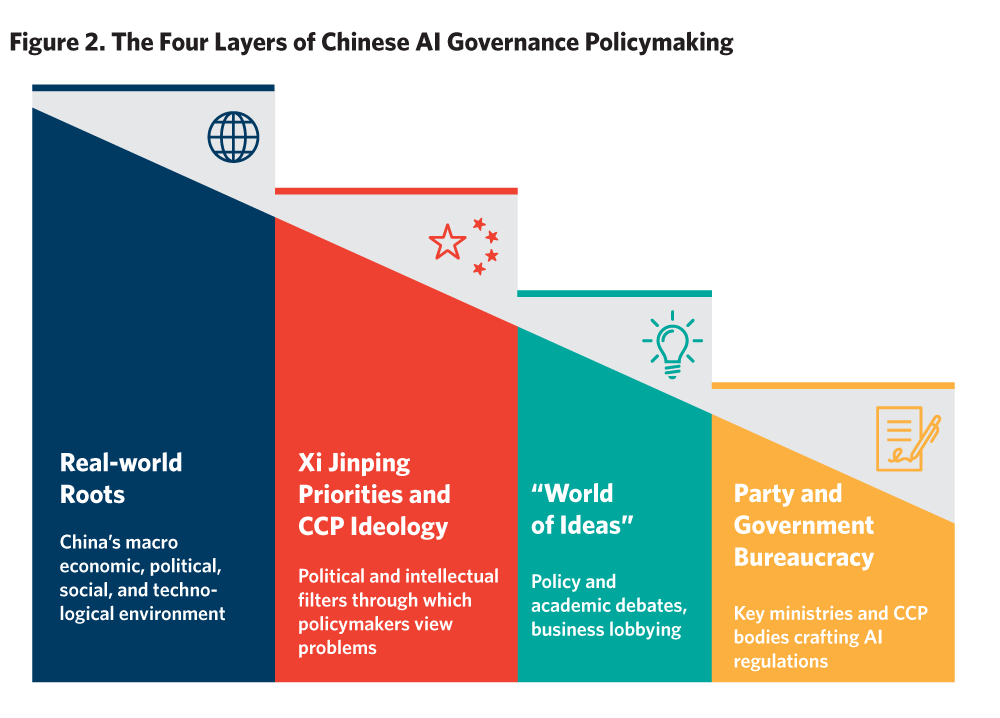
China's ambition to lead in AI by 2030 faces significant hurdles, particularly due to stringent U.S. export controls on advanced semiconductors. Despite these restrictions, Chinese firms like DeepSeek have shown remarkable progress, developing models that rival U.S. counterparts, albeit often requiring more computational power. This has spurred China's drive for technological self-sufficiency, with substantial investments in domestic chip manufacturing and AI infrastructure. However, China still relies on smuggled U.S. chips, and its domestic chip production, while improving, lags behind the most advanced global standards.
The massive computational demands of AI models are driving significant energy consumption, particularly by hyperscale data centers. These facilities require immense and reliable power, leading many to consider natural gas as a primary energy source. The consistent and on-demand nature of natural gas power plants offers stability that renewable energy sources alone cannot always provide, making it an attractive option for ensuring uninterrupted operation of critical AI infrastructure. This choice reflects the industry's need for stable power to support continuous AI training and deployment.
As AI capabilities advance, especially towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the methods for measuring its societal and economic impact become increasingly complex. AGI, defined as AI possessing human-level cognitive abilities across a wide range of tasks, presents challenges in assessment beyond traditional metrics. Its potential influence spans economic productivity, labor markets, and ethical considerations, necessitating comprehensive frameworks to understand its far-reaching implications. The discussion around AGI's impact underscores the need for robust evaluation methodologies as the technology evolves.