Microsoft's LongRoPE2 Achieves 80x Training Efficiency for 128K LLM Context Windows
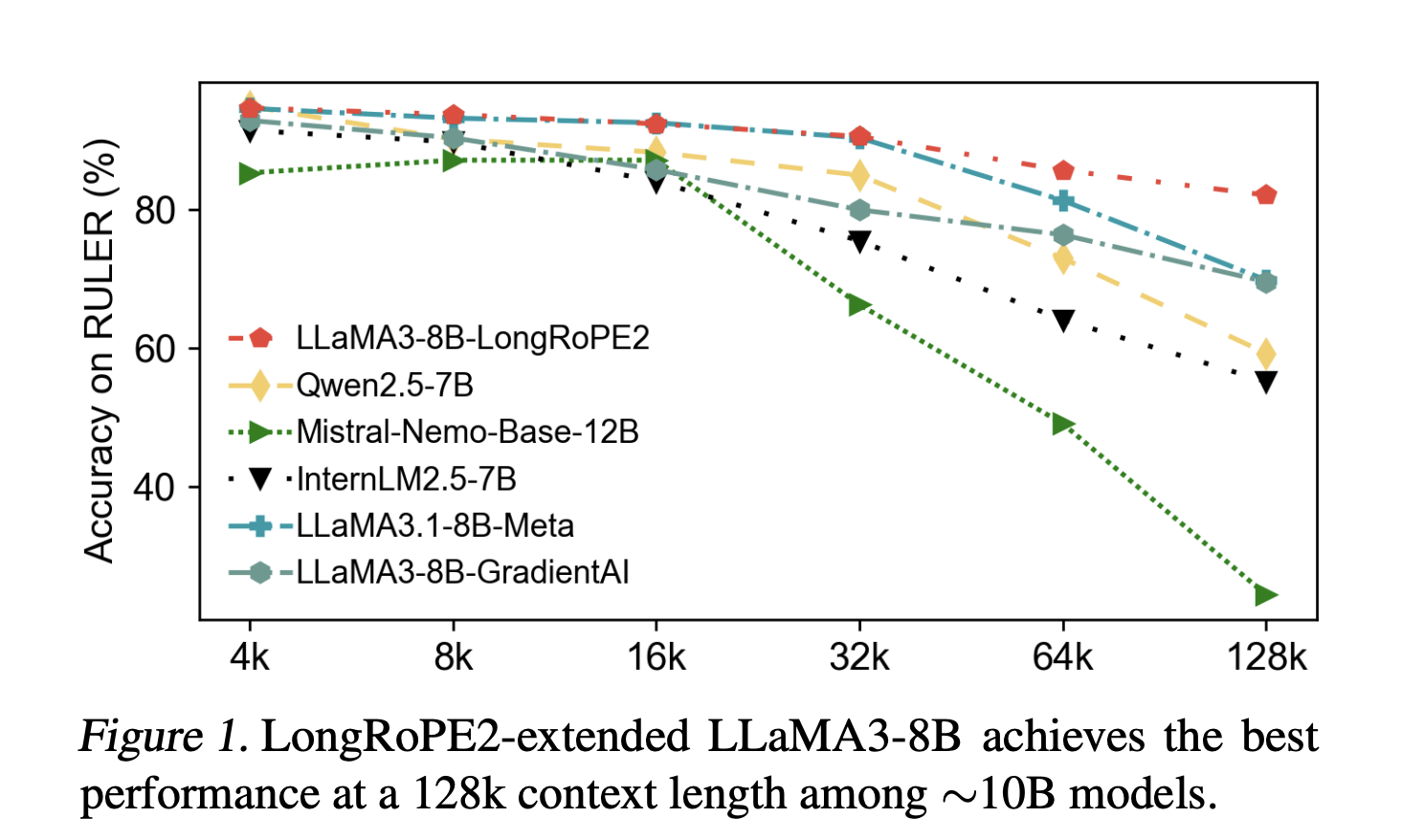
Microsoft researchers have unveiled a significant advancement in Large Language Models (LLMs) with their new method, LongRoPE2, enabling an unprecedented 80-fold increase in training efficiency for extended context windows. The paper, "LongRoPE2: Near-Lossless LLM Context Window Scaling," details a novel approach that allows models like LLaMA3-8B to process 128,000 tokens while retaining over 98.5% of their original short-context performance. This breakthrough was celebrated by Teortaxes▶️, known as @kalomaze on social media, who remarked, "Another @kalomaze victory."
The core innovation behind LongRoPE2 addresses the persistent out-of-distribution (OOD) issues in Rotary Positional Embeddings (RoPE), which typically hinder LLMs from effectively handling longer sequences. The team identified that insufficient training in higher RoPE dimensions was a key limitation. Their solution involves an evolutionary search-guided RoPE rescaling algorithm combined with a mixed context window training approach, fine-tuning model weights for both long and short contexts.
A striking aspect of LongRoPE2 is its remarkable efficiency. The method extends LLaMA3-8B to a 128K effective context length using only 10 billion training tokens. This contrasts sharply with Meta's LLaMA3.1 approach, which required 800 billion tokens for a similar extension, often failing to reach the target effective context length. This substantial reduction in computational resources marks a significant step towards more accessible and sustainable LLM development.
The tweet also referenced an investigation into Native Sparse Attention (NSA), noting its flaw where "chunk selection is not end-to-end learnable." While LongRoPE2 primarily focuses on RoPE, this commentary highlights a broader challenge within the LLM community regarding efficient long-context processing. DeepSeek-AI's Native Sparse Attention, detailed in a separate paper, aims to overcome such limitations by being a hardware-aligned and natively trainable sparse attention mechanism.
LongRoPE2's ability to achieve near-lossless context extension with drastically lower training costs positions it as a critical development in the LLM landscape. This efficiency not only reduces the operational expenses associated with developing powerful AI models but also paves the way for broader applications requiring extensive contextual understanding, such as advanced document analysis and complex reasoning tasks.