WebAssembly and WebGPU Drive Significant Performance Gains, Bridging Gap with Native Applications
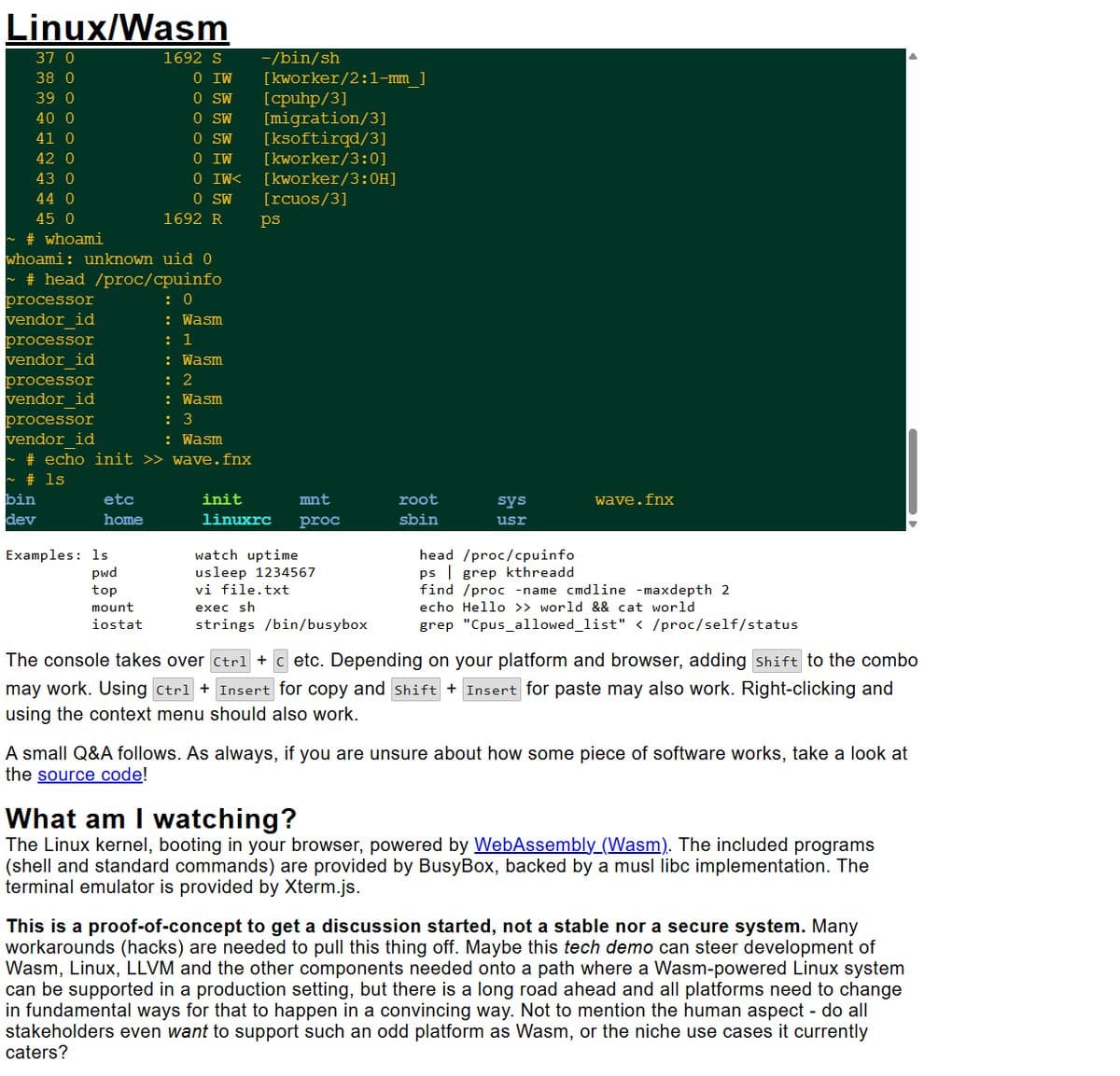
A recent social media post by developer wavefnx has highlighted the stark performance differences between GPU-driven local applications and JavaScript-heavy web applications. "It's almost impossible to use a webapp after using GPU driven local applications with zero javascript," wavefnx stated, emphasizing a preference for speed with the phrase "gotta go fast." This sentiment resonates with a growing industry push to enhance web application performance to rival that of native software.
Native applications, designed for specific operating systems, inherently offer superior performance due to direct access to device hardware and optimized code execution. In contrast, traditional web applications, heavily reliant on JavaScript running within a browser, often face limitations in speed, responsiveness, and access to system resources. This disparity has historically positioned web apps as less capable for demanding tasks.
However, advancements in web technologies like WebAssembly (Wasm) and WebGPU are rapidly closing this performance gap. WebAssembly enables code written in languages such as C++ or Rust to run in web browsers at near-native speeds, significantly improving the execution of CPU-intensive tasks. Recent upgrades, including WebAssembly 3.0, have introduced features like 64-bit address spaces and garbage collection, further expanding its capabilities for larger, more complex applications.
Complementing WebAssembly, WebGPU is an emerging API that provides web applications with direct access to a device's Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). This allows for high-performance graphics rendering and parallel computations, crucial for applications involving artificial intelligence, machine learning, and complex simulations. Studies indicate that offloading computations to WebGPU can achieve an approximately 50-fold reduction in execution time for certain tasks, while SIMD-enabled WebAssembly modules have shown up to an 1.64 times improvement over optimized JavaScript implementations in specific benchmarks.
These technologies are transforming the landscape of web development, enabling developers to build web applications that deliver rich, high-performance user experiences previously exclusive to native platforms. The continuous evolution of WebAssembly and WebGPU signifies a future where the web can host increasingly sophisticated and responsive applications, directly addressing the performance concerns voiced by developers like wavefnx.